Healthcare Emissions
Carbon footprints stemming from health care have been found to be variable across the globe;
-
3% of the total national CO2 equivalent (CO2e) emissions in England, to
-
10% of the national CO2e emissions in the USA
(refer ).
While Healthcare CO2-e emission data in Australia is limited, it is estimated that Healthcare contributes to approximately 7% of Australia’s total CO2-e emissions.
The following information has been extracted from The Carbon Footprint of Australian Healthcare (A.Malik, M.Lenzen, S.McAlister, and F.McGain)
Because of Australia’s lack of CO2-e emission data for the healthcare sector, reference can be made to global data provided by Healthcare Without Harm, and health services that are comparable to that of Australia, such as the NHS in the U.K., which is currently leading the way in making data available for delivering a net zero health service.
The economic input-output lifecycle assessment related economic expenditure to CO2-e emissions.
Expenditure data was obtained from the 15 sectors of the Australian Institute of Health and Welfare for the financial year 2014–15.
The Australian Industrial Ecology Virtual Laboratory (IELab) data was used to obtain CO2e emissions per AUS$ spent on health care.
In 2014–15 Australia spent $161·6 billion on health care which corresponds to about 35,772 kilotonnes of CO2-e emissions.
The article reports that Australia’s total CO2-e emissions in 2014–15 were 494,930 kilotonnes, thus health care represented 7% (35,772 kilotonnes) of total CO2-e emissions in Australia.
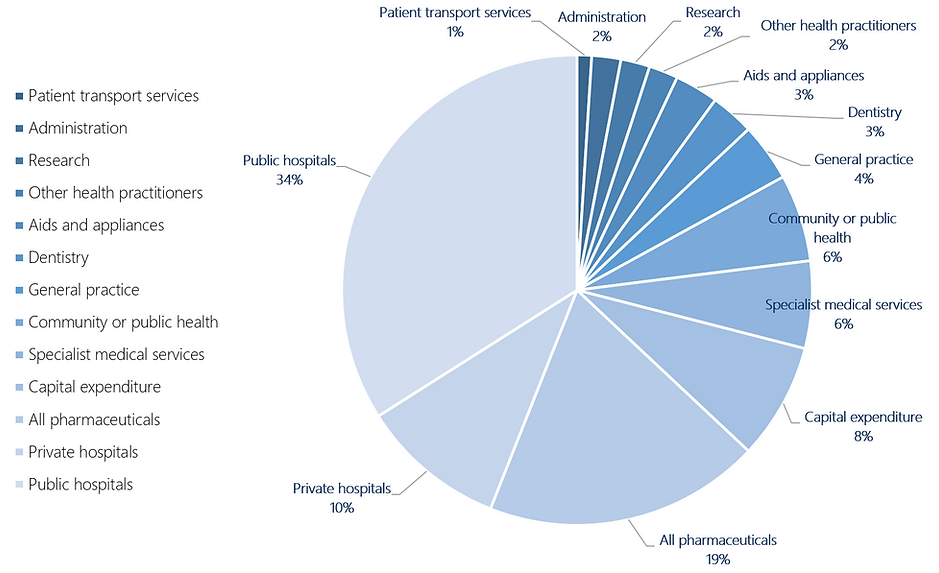
The five most important sectors within health care in decreasing order of total CO2-e emissions were:
-
Public hospitals (12295 [34%] of 35772 kilotonnes CO2e),
-
Private hospitals (3635 kilotonnes [10%]),
-
Other medications (3347 kilotonnes [9%]),
-
Benefit-paid drugs (3257 kilotonnes [9%]), and
-
Capital expenditure for buildings (2776 kilotonnes [8%]).
Figure - Total and Relative CO2e Emissions for Healthcare Expenditure Categories
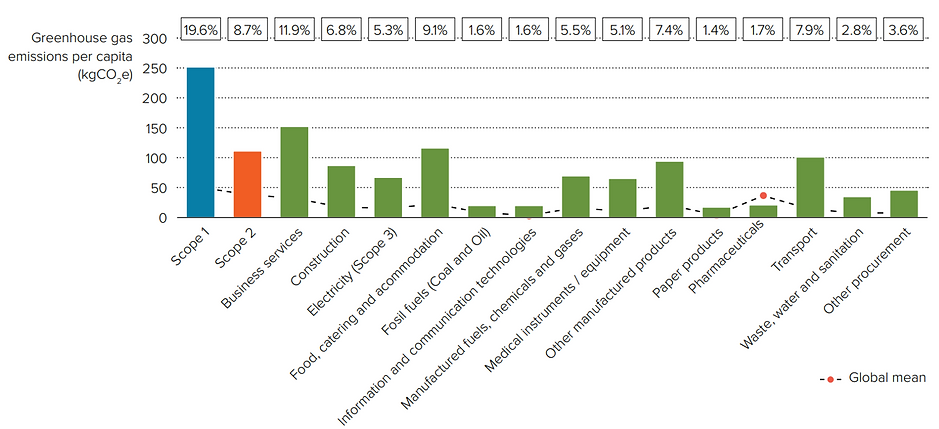
The following graph shows Australia's overall Healthcare Footprint by Scope.
As can be seen, Scope 3 is the largest contributor and requires a holistic solution. Scope 1 and 2 combined are still significant and need to be addressed in order to meet our 2030 and 2050 requirements.

The breakdown for each scope is shown below: